Quizlet What Best Describes the Action of Nsaids
Paracetamol is an NSAID with a comparatively low anti-inflammatory effect compared to other NSAIDs. What is the name of the structure.

Musculoskeletal Fnp Review Fitzgerald Flashcards Quizlet
NSAIDs reduce the therapeutic effect of SSRIs.

. Cytoprotective and COX2 Selective inducible and on when turned on. Steroids are man-made drugs. Which term best describes the mechanism of action for fluoroquinolones.
NSAIDs are not recommended during pregnancy. Traditionally the analgesic action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs has been explained on the basis of their inhibition of the enzymes that synthesise prostaglandins. Primary use of NSAIDS.
-Decreases platlet adhesiveness and direct membrane action. The second statement is true. Parathyroid hormone and estrogen may also be of value.
Pharmacology Terms Quizlet Drug of the Week A pharmacological action of a particular agent has an absolute requirement for a definite effect and cannot be stated as an approximate rating1 This may be either a description or an estimate of the actual structure or activity of the agent to be used in making the actual drug. NSAIDs have a hypocoagulability effect. NSAIDs also work well fighting back pain menstrual cramps and headaches.
A variety of NSAIDs are available including at. The analgesic anti-pyretic and anti-inflammatory actions of the NSAIDs result from the same mechanism as aspirinthe inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by inhibiting cyclooxygenase. NSAIDs block the production of certain body chemicals that cause inflammation.
A Alkylating agent b Antisense agent c Chain cutter d Topoisomerase poison Question 3 The following antibacterial agent was used in the Second World War. Infiltration of leukocytes and phagocytic cells to the site of inflammation. A C D E Calcium Evista Fosamax Actonel and Calcitonin can be used by postmenopausal women to treat or prevent osteoporosis.
Nonopioid or nonnarcotic analgesics act primarily at the peripheral nerve endings. NSAIDs reduce kidney blood flow and thereby decrease the efficacy of diuretics and inhibit the elimination of lithium and methotrexate. RA OA pain and fever.
Mechanism of Action. NSAIDs work by blocking your bodys production of the chemicals associated with pain and inflammation. If possible NSAIDs should be avoided in HF patients in order to avoid exacerbations of HF Which best describes the action of ACE inhibitors on the failing heart.
NSAIDS can have analgesic activity via. They are some of the most commonly used medications in adults. NSAIDs may provide pain relief.
NSAIDs are good at treating pain caused by slow tissue damage such as arthritis pain. The first statement is false. NSAIDs cause decreased ability to form blood clots which can increase the risk of bleeding when combined with other drugs that also decrease blood clotting such as warfarin.
Cyclooxygenase is required to convert arachidonic acid into thromboxanes prostaglandins and prostacyclins. This helps to block pain and inflammation. The main mechanism of action of NSAIDs is the inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase COX.
This just covers the points that were emphasized in the lecture according to my notes - take it or leave it - but I hope it helps. Penicillin NSAIDs and calcium are not considered high alert drugs. -More potent and platlets are more sensitive to it than all other NSAIDS.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs are among the most widely used medications in the world because of their demonstrated efficacy in reducing pain and inflammation. NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandin synthesis by blocking the action of cyclooxygenase. NSAIDs increase renal blood flow.
In the periphery via blocking transmission or perception. NSAIDs block enzymes called. A student nurse asks the nurse why acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs help to reduce cancer pain.
NSAIDs work like corticosteroids also called steroids without many of the side effects of steroids. They serve to inhibit the biosynthesis of prostaglandins by blocking COX 1 Nonselective bothconstitutional and always on. What is the term for a drug that has the same action as a naturally occurring body hormone or enzyme.
However it is clear that NSAIDs exert their analgesic effect not only through peripheral inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis but also through a variety of other peripheral and central mechanisms. 1 In periphery they decrease nocioceptive response to painful stimuli 2 In CNS they block incoming pain signals from moring to higher in the brain. Which term describes how the body affects drug activity.
Primary mechanism of action of NSAIDs is. Pharm - Exam 3 - Nsaids. However these medications neither prevent nor treat osteoporosis.
The primary action of the nonopioid analgesics is depression of the central nervous system. -Permanantly inactives PG synthesis until replaced by new synthesis. -Better antithrombotic than other NSAIDS.
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen lead to increased fluid retention and increased blood pressure. This inhibition is competitively reversible as opposed to the mechanism of aspirin which is irreversible inhibition. 1 Their efficacy has been documented in a number of clinical disorders including osteoarthritis rheumatoid arthritis ankylosing spondylitis gout dysmenorrhea dental pain and headache.
Match the description with the stage of inflammation. Mechanism of Action of NSAIDs. The inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis reduces the perception of pain.
Acute transient phase delayed subacute phase and chronic proliferative phaseA. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs NSAIDs are medications used to relieve pain and to reduce inflammation. Most NSAIDs act as nonselective inhibitors of the enzyme cyclooxygenase COX inhibiting both the cyclooxygenase-1 COX-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 COX-2 isoenzymes.
The therapeutic effects of NSAIDs are attributed to the lack of these eicosanoids.

Is Ii Med Chem Lecture 1 Flashcards Quizlet

Cns Headache Pharmacology Gayer Flashcards Quizlet

Rosh Review Medical Knowledge Family Nurse Practitioner Medical Education

Ipap Pharm Ii Test 3 Headaches Flashcards Quizlet
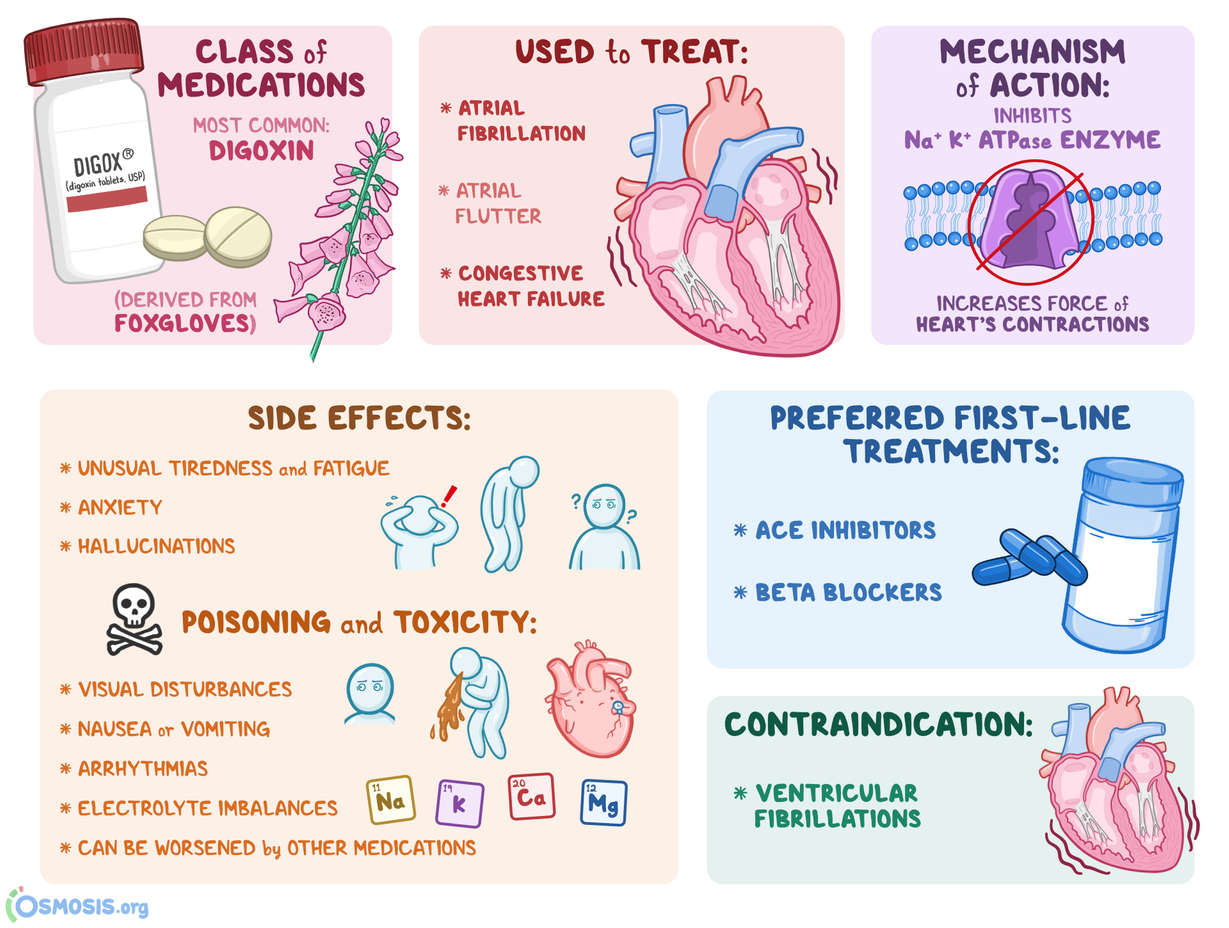
Cardiac Glycosides What Are They What Are They Used For How Do They Work Side Effects And More Osmosis

Ipap Pharm Ii Test 3 Headaches Flashcards Quizlet

Anti Inflammatory Drugs Flashcards Quizlet

Y2 Lcrs Pharmacology And Therapeutics Flashcards Quizlet

Anti Inflammatory Questions Without Dmards And Anti Gout Drugs Flashcards Quizlet

Pharm 2 Questions Flashcards Quizlet
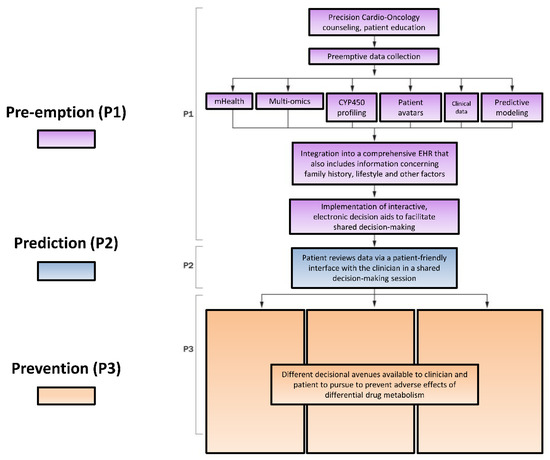
Ijms Free Full Text The Role Of Cyp450 Drug Metabolism In Precision Cardio Oncology Html

Musculoskeletal Fnp Review Fitzgerald Flashcards Quizlet

Pharm Block 2 Flashcards Quizlet

Ipap Pharm Ii Test 3 Headaches Flashcards Quizlet

Pain Control D2 Spring Par 2 Flashcards Quizlet

B16 5 Rheumatoid Arthritis Gout Flashcards Quizlet




Comments
Post a Comment